
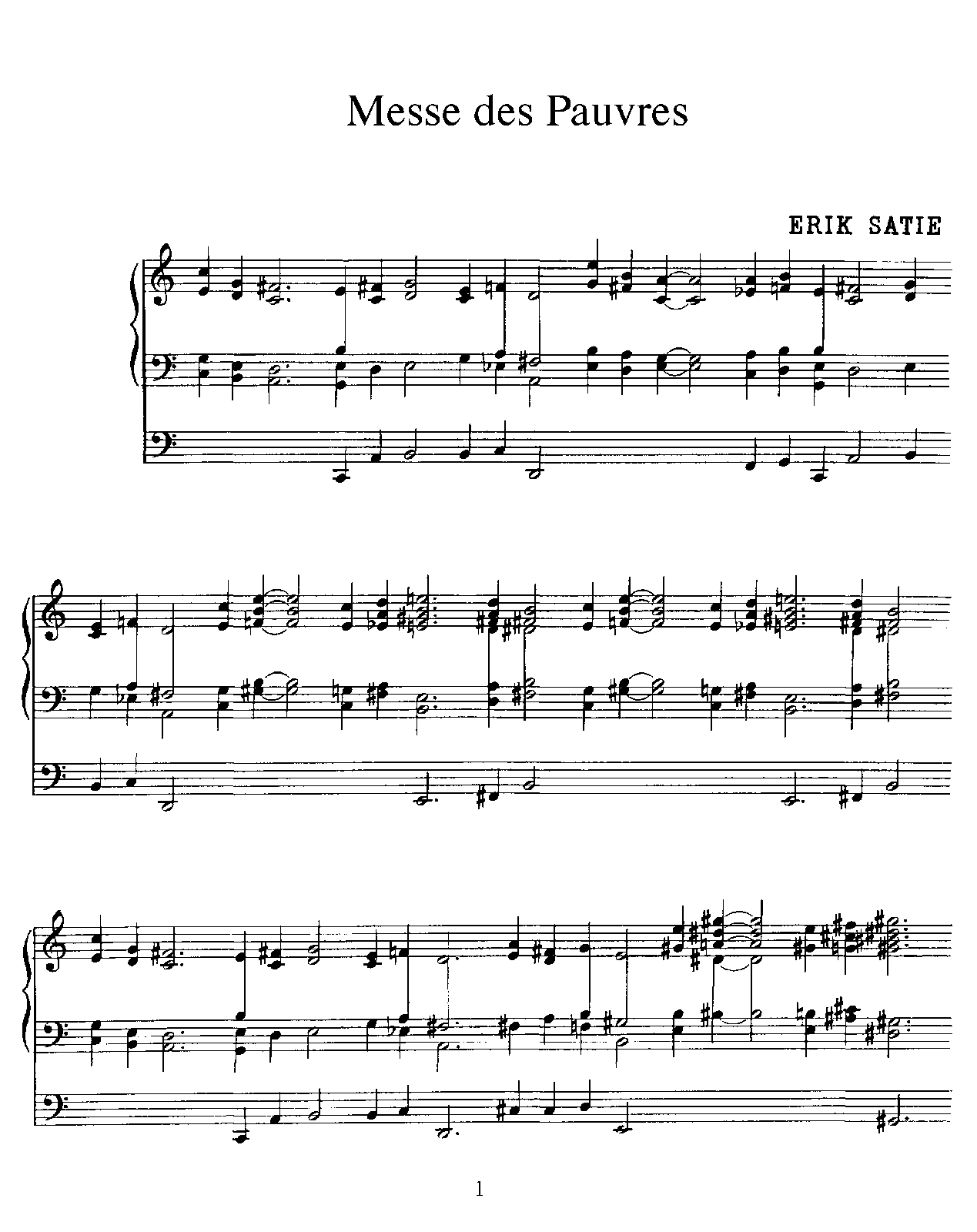

Menus propos enfantins serves as a sort of introduction. Each set is built on a different five-finger scale, using only the white keys of the piano. These are genuine children's pieces, crafted for small hands, with simple themes that can be easily learned. This side of Satie found its most direct creative expression in the Enfantines, music his first biographer Pierre-Daniel Templier described as not "about children, or for children, but of a child." From 1908 to 1910 he ran a charity group in his hometown of Arcueil to take orphans and poorer boys and girls on country outings and on Sunday mornings he gave them solfège lessons and improvised melodies with funny titles to make them laugh. He identified with children, and his respect for their innocence and naiveté has been related to his own quest for purity and directness in music. Many of Satie's contemporaries spoke of his essentially childlike nature. Two additional sets were published posthumously. The Enfantines are three sets of beginner piano pieces by Erik Satie, "written with the aim of preparing children for the sound patterns of modern music." They were composed in October 1913 and published the following year.
#Composer satie full#
When it was presented in New York in 1963, five different pianists had to play in relays all night long to give it a full performance.Erik Satie, self-portrait sketch with his quote, "I came into the world very young, in an age that was very old" Satie wrote a piece for piano with one hundred and eighty notes, which had to be repeated eight hundred and forty times. Satie died in 1925, his music faded into obscurity for almost 50 years until the 1960s when it was rediscovered by the modern minimalist composer John Cage, who found Satie an inspiration and influence on his own music. The score was compelling, and the inclusion of guns, car horns, sirens, and typewriters was so innovative and raucous as to cause an opening night riot that brought Satie to the public's attention. He finally achieved a degree of success that had long eluded him with ‘Parade’, a collaboration with Pablo Picasso, Jean Cocteau, and the director of Les Ballet Russes de Monte Carlo, Serge Diaghilev. Some of his odd antics included never allowing anyone to enter his apartment, and some of the instructions he asked performers to follow during a performance of a work would be, playing a piece of music as ‘light as an egg’. Satie was also an influence on the Impressionist composer Debussy, a life-long friend.īesides the influence he had on his contemporaries, he was best known for his eccentric behaviour. Following Satie’s lead, they tried to write simple and clear music. Only a select few from music circles of the time knew that he was an influence on the composer group Les Six, which included Darius Milhaud and Francis Poulenc. Today he is best known to us through his well-loved Gymnopédies, the small melancholic piano pieces from 1890, but at the time of his death in 1925, Satie was barely known beyond the city limits of Paris.Įrik Satie, the well-loved yet eccentric composer of piano miniatures, was born on May 17th 1866 in Honfleur, Normandy, the son of a French music publisher.Īged 18, Satie moved to Paris where he studied briefly at the Paris Conservatory and found his first musical voice as the official composer of the Rosicrucian movement. Erik Satie (1866–1925) was a French composer and pianist.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
